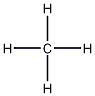
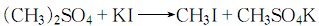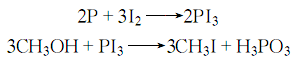Structural formula
| Business number | 01HM |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH5N |
| Molecular weight | 31.06 |
| label |
aminomethane, monomethylamine, aminomethane |
Numbering system
CAS number:74-89-5
MDL number:MFCD00008104
EINECS number:200-820-0
RTECS number:PF6300000
BRN number:741851
PubChem number:24857793
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: colorless gas with ammonia-like odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -93.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): -6.3[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.66 (25℃)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 1.08[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 304 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1085.6[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 157.6[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 7.614[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient :-0.57[10]
11. Flash point (℃): 0 (CC)[11]
12 .Ignition temperature (℃): 430[12]
13. Explosion limit (%): 21[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 5[14]
15. Solubility: easily soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, benzene, acetone, etc. [15]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16] LC50: 2400mg/m3 (mouse inhalation, 2h)
2. Irritation[17]
Transdermal use in rabbits: 1.0ml of 40% solution can cause skin irritation and necrosis in rabbits.
Rabbit eye: 4% solution can cause corneal damage in rabbits.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [18] Guinea pigs first inhaled 0.25mg/L for 93 days, and then inhaled 0.5mg/L for 30 days. It begins with transient irritation and eventually leads to failure and dysfunction of hepatic prothrombin formation.
4. Mutagenicity[19] Rat inhalation 10μg/m3positive lethality test, 3mmol /L can cause lymphocyte mutations in mice.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[20]
LC50: 10~30mg/L (96h) (fish)
EC50: 480mg/L (48h) (Daphnia)
2. Biodegradability [21] 96% degradation in OECD screening test.
3. Non-biodegradability[22] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pcs/cm3, the degradation half-life is 18h (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 10.21
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 48.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 100.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 18.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 4.05
Compute chemical data
1.HydrophobicReference value for �� calculation (XlogP): -0.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26
7. Number of heavy atoms: 2
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 2
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Methylamine aqueous solution or alcohol solution are both flammable liquids. Because it has a low flash point, is volatile, toxic, and can form explosive mixtures with air, avoid direct sunlight and devices prone to static electricity. Methylamine is corrosive to copper or copper alloys, aluminum, tin and galvanized iron. Flammable.
2. Typical reactions with primary amines having chemical properties:
① The aqueous solution is alkaline, and reacts with inorganic acids, organic acids, acidic aromatic nitro compounds, etc. to form compounds with a certain melting point of salt. It forms complex salts with heavy metal chlorides such as copper and silver.
② Acylation reaction occurs with acid chloride, acid anhydride, etc. to generate N-substituted amide. The salt formed with carboxylic acid also generates N-substituted amide upon dehydration. Reacts with benzene sulfonyl chloride to generate N-substituted benzenesulfonamide.
③ By reacting with hydrocarbylation reagents such as halogenated hydrocarbons, alcohols, phenols or amine salts, the hydrogen atoms on the nitrogen can be replaced by hydrocarbon groups.
④ Addition reactions can occur with cyanic acid, carbon disulfide, nitriles, epoxides, etc.
⑤ Primary amine reacts with aliphatic or aromatic and dehydrates to form Schiff base.
⑥ Primary amines are relatively stable to acidic potassium permanganate, but are easily oxidized by alkaline potassium permanganate to generate aldehydes or carboxylic acids. Under the action of persulfuric acid, hydrogen peroxide, and organic peroxyacid, amine oxygen-containing compounds are obtained.
⑦ Reacts with nitrous acid to quantitatively generate nitrogen gas.
⑧ Heating with chloroform and potassium hydroxide alcohol solution to generate isonitrile.
⑨ Reacts with Grignard reagent to generate hydrocarbons.
In addition, methylamine undergoes pyrolysis at 550~670°C to generate ammonia, hydrogen cyanide, methane, hydrogen and nitrogen. It can also decompose under ultraviolet light to generate gases and liquids such as methane and nitrogen.
3. Stability[23] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[24] Acids, halogens, acid anhydrides, strong oxidants, chloroform
5. Polymerization hazard[25] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[26] Ammonia
Storage method
Storage Precautions[27] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse dedicated to flammable gases. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, halogens, etc. and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with leakage emergency response equipment.
Synthesis method
1. Industrially, methylamine is synthesized by passing methanol and ammonia through a converter equipped with an activated alumina catalyst at high temperature. However, the methylation reaction does not stop at the first methylamine stage, so the resulting A mixture of methylamine, dimethylamine and trimethylamine. Controlling the ratio of methanol and ammonia to make excess ammonia, adding water and circulating trimethylamine is beneficial to the generation of monomethylamine and dimethylamine. When the amount of ammonia is 2.5 times that of methanol, the reaction temperature is 425°C, and the reaction pressure is 2.45MPa, Mixed amines with 10-12% monomethylamine, 8-9% dimethylamine and 11-13% trimethylamine can be obtained. Since trimethylamine forms an azeotrope with ammonia and other methylamines under normal pressure, the reaction product is separated using a combination of pressure distillation and extractive distillation. Calculated to produce 1 ton of mixed methylamine, 1500kg of methanol and 500kg of liquid ammonia are required. According to relevant literature reports, changing the ratio of methanol and ammonia is an effective method to obtain the desired product. When the ratio of methanol and ammonia is 1:1.5, it is the best condition for generating trimethylamine, and the ratio of methanol and ammonia is 1:4. This is the best condition for generating monomethylamine.
Refining method: It often contains impurities such as dimethylamine, trimethylamine, methanol, and ammonia. During refining, the methylamine aqueous solution is first extracted and distilled to remove trimethylamine, and then dimethylamine is removed by fractional distillation. Methylamine hydrochloride can also be extracted with dry chloroform for more than 30 hours to remove higher amines, and then refined by recrystallization with ethanol (m.p. 225~226°C). Or first fractionate the condensate produced by methylamine and formaldehyde, and decompose the distillate in butanol with hydrochloric acid. The resulting hydrochloride salt was recrystallized from ethanol. The refined methylamine hydrochloride thus obtained is decomposed with excess potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide, and the gaseous methylamine obtained is dehydrated by solid potassium hydroxide, and then traces of ammonia are removed with silver oxide. Then use dry ice and diethyl ether to cool and liquefy, and dry the sodium fluorenone to obtain pure methylamine. Other refining methods include recrystallizing methylamine hydrochloride with butanol, absolute ethanol or a mixture of methanol and chloroform, washing with chloroform to remove trace amounts of dimethylamine hydrochloride, and then drying in a vacuum dryer. .
2. Aqueous solution. Mix 40% methylamine aqueous solution with distilled water to make a 30% methylamine solution.
![]()
Purpose
Used in the synthesis of rubber vulcanization accelerators, dyes, medicines, pesticides, surfactants, etc. [28]
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44903extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/827extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40065extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/low-odor-amine-catalyst-pt305-reactive-amine-catalyst-pt305/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fascat8201-catalyst-2/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1095extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/jeffcat-dmp-lupragen-n204-pc-cat-dmp/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40292extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/935extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/New-generation-sponge-hardener.pdf